Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
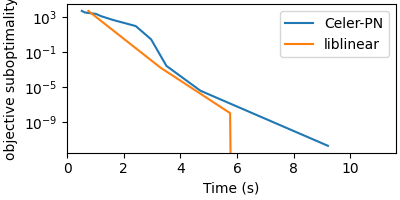
Compare LogisticRegression solver with sklearn’s liblinear backend¶
file_sizes: 0%| | 0.00/26.8M [00:00<?, ?B/s]
file_sizes: 0%| | 24.6k/26.8M [00:00<03:58, 112kB/s]
file_sizes: 0%| | 49.2k/26.8M [00:00<03:59, 112kB/s]
file_sizes: 0%| | 106k/26.8M [00:00<02:28, 180kB/s]
file_sizes: 1%|▏ | 221k/26.8M [00:00<01:24, 314kB/s]
file_sizes: 2%|▍ | 451k/26.8M [00:01<00:45, 576kB/s]
file_sizes: 3%|▉ | 909k/26.8M [00:01<00:23, 1.09MB/s]
file_sizes: 7%|█▊ | 1.83M/26.8M [00:01<00:11, 2.09MB/s]
file_sizes: 14%|███▌ | 3.66M/26.8M [00:01<00:05, 4.04MB/s]
file_sizes: 20%|█████ | 5.23M/26.8M [00:01<00:04, 5.01MB/s]
file_sizes: 29%|███████▋ | 7.86M/26.8M [00:02<00:02, 7.10MB/s]
file_sizes: 35%|█████████▏ | 9.43M/26.8M [00:02<00:02, 7.13MB/s]
file_sizes: 45%|███████████▋ | 12.1M/26.8M [00:02<00:01, 8.54MB/s]
file_sizes: 51%|█████████████▏ | 13.6M/26.8M [00:02<00:01, 8.15MB/s]
file_sizes: 61%|███████████████▊ | 16.2M/26.8M [00:03<00:01, 9.25MB/s]
file_sizes: 67%|█████████████████▎ | 17.8M/26.8M [00:03<00:01, 8.64MB/s]
file_sizes: 76%|███████████████████▊ | 20.4M/26.8M [00:03<00:00, 9.61MB/s]
file_sizes: 86%|██████████████████████▍ | 23.1M/26.8M [00:03<00:00, 10.3MB/s]
file_sizes: 92%|███████████████████████▉ | 24.6M/26.8M [00:03<00:00, 9.36MB/s]
file_sizes: 100%|██████████████████████████| 26.8M/26.8M [00:03<00:00, 6.72MB/s]
import time
import warnings
import numpy as np
from numpy.linalg import norm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import linear_model
from libsvmdata import fetch_libsvm
from celer import LogisticRegression
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", message="Objective did not converge")
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", message="Liblinear failed to converge")
X, y = fetch_libsvm("news20.binary")
C_min = 2 / norm(X.T @ y, ord=np.inf)
C = 20 * C_min
def pobj_logreg(w):
return np.sum(np.log(1 + np.exp(-y * (X @ w)))) + 1. / C * norm(w, ord=1)
pobj_celer = []
t_celer = []
for n_iter in range(10):
t0 = time.time()
clf = LogisticRegression(
C=C, solver="celer-pn", max_iter=n_iter, tol=0).fit(X, y)
t_celer.append(time.time() - t0)
w_celer = clf.coef_.ravel()
pobj_celer.append(pobj_logreg(w_celer))
pobj_celer = np.array(pobj_celer)
pobj_libl = []
t_libl = []
for n_iter in np.arange(0, 50, 10):
t0 = time.time()
clf = linear_model.LogisticRegression(
C=C, solver="liblinear", penalty='l1', fit_intercept=False,
max_iter=n_iter, random_state=0, tol=1e-10).fit(X, y)
t_libl.append(time.time() - t0)
w_libl = clf.coef_.ravel()
pobj_libl.append(pobj_logreg(w_libl))
pobj_libl = np.array(pobj_libl)
p_star = min(pobj_celer.min(), pobj_libl.min())
plt.close("all")
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4, 2), constrained_layout=True)
plt.semilogy(t_celer, pobj_celer - p_star, label="Celer-PN")
plt.semilogy(t_libl, pobj_libl - p_star, label="liblinear")
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("Time (s)")
plt.ylabel("objective suboptimality")
plt.show(block=False)
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 20.601 seconds)